
Ever wondered how clean water arrives at your tap, or how vibrant colors stay on your favorite shirt? The answer often involves aluminum sulfate—a versatile, widely used inorganic salt. So, what is aluminum sulfate? In simple terms, it’s a white, odorless crystalline compound made from aluminum, sulfur, and oxygen. Known by several names, you’ll hear it called “alum” or “papermaker’s alum,” but keep in mind: the term “alum” can also refer to other related compounds, so context matters [source].
This compound plays a crucial role in everyday life and industry. You’ll find it:
Sounds complex? Don’t worry—this article breaks it all down. We’ll explore the aluminum sulfate definition, its chemical properties, and how its unique formula shapes its many uses. You’ll also discover related compounds, such as sodium and potassium aluminum sulfate, and learn how this unsung chemical hero impacts everything from water treatment to gardening. Ready to unlock the science behind aluminum sulfate? Let’s dive in!

When you picture a chemical that quietly supports everything from clean water to crisp paper, aluminum sulfate is a prime example. But what exactly makes it so special? Let’s break down the aluminum sulfate properties and why they matter in everyday applications.
Aluminum sulfate is classified as an inorganic salt. This means it’s formed from the reaction of an acid (typically sulfuric acid) with a base (like aluminum hydroxide). Its structure is made up of aluminum, sulfur, and oxygen atoms arranged in a specific ratio. In its pure form, it’s most often found as a white, odorless crystalline solid—think of small, glistening crystals or a fine powder [source].
Wondering what you’d notice if you saw or handled aluminum sulfate? Here are its most notable features:
Aluminum sulfate’s ability to dissolve easily in water and create acidic conditions explains why it’s so effective in coagulating impurities during water purification and in helping dyes stick to fabrics. Its hygroscopic property means you’ll want to store it in sealed containers to prevent it from absorbing moisture and degrading.
Curious about the science behind its formula? Up next, we’ll unpack the chemical structure of aluminum sulfate and see how its elemental makeup shapes its unique behavior.
Ever glanced at a bag of pool chemicals or a gardening supply and wondered, “What is the formula for aluminum sulfate?” The answer is both simple and revealing: Al2(SO4)3. Let’s break down what this really means—and why it matters for everything from water treatment to paper making.
At first glance, the formula Al2(SO4)3 might look intimidating. But once you understand the pieces, it’s easy to see how they fit together:
So, the full formula tells us that two aluminum ions balance the charge of three sulfate ions, creating a neutral compound. This balance is crucial for the stability and solubility of the salt in water.
When you see aluminum sulfate in the lab, you’ll often notice a slightly different formula: Al2(SO4)3·18H2O. This isn’t a typo—it’s the hydrated form, known as aluminum sulfate octadecahydrate. Here’s how it works:
Why does this matter? The water of crystallization affects the compound’s weight, solubility, and how it behaves in chemical reactions. In practical terms, you’ll find the hydrated form in most commercial and industrial uses because it’s more stable and easier to handle.
Imagine you have a single unit of aluminum sulfate:
This precise arrangement is what gives aluminum sulfate its unique properties—like its ability to dissolve rapidly in water and form acidic solutions, making it ideal for coagulating impurities in water treatment or acting as a mordant in dyeing.
Understanding what is aluminum sulfate formula isn’t just about memorizing symbols—it’s about seeing how these elements work together to create a compound that’s essential for so many industries. Next, we’ll dive deeper into the numbers and see how to calculate its molar mass, a key step in using it effectively in science and industry.

Ever tried to mix chemicals for a science project or wondered how much of a compound you actually need for a reaction? That’s where understanding molar mass—the mass of one mole of a substance—becomes essential. So, what is the molar mass of aluminum sulfate, and how do you figure it out?
Molar mass is the weight (in grams) of one mole (6.022 × 1023 particles) of a substance. It’s measured in grams per mole (g/mol). Knowing the molar mass is crucial in chemistry for tasks like:
Let’s walk through the process using aluminum sulfate’s formula: Al2(SO4)3.
To calculate the molar mass, you’ll need the atomic masses of each element and the number of atoms in the formula. Here’s how it breaks down:
| Element | Number of Atoms | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Total Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum (Al) | 2 | 26.98 | 53.96 |
| Sulfur (S) | 3 | 32.06 | 96.18 |
| Oxygen (O) | 12 | 16.00 | 192.00 |
Now, add up the total mass from each element:
Total molar mass: 53.96 + 96.18 + 192.00 = 342.14 g/mol
So, the molar mass of Al2(SO4)3 is 342.14 g/mol [reference].
Sometimes, you’ll encounter aluminum sulfate as a hydrate, most commonly Al2(SO4)3·18H2O. To find the molar mass of this form, simply add the mass of 18 water molecules (18 × 18.02 g/mol) to the anhydrous molar mass:
That’s a significant increase—so always check which form you’re using before measuring!
Understanding what is the molar mass of aluminum sulfate and how to calculate it ensures you get accurate results, whether you’re purifying water, making paper, or conducting lab experiments. Next, let’s look at how this compound is produced and why the purity of its components is so important for industrial applications.
Ever wondered what is aluminum sulfate made of or how this essential compound gets from raw earth to your water treatment plant or paper mill? Let’s break down the process, step by step, and see why purity and quality matter so much—especially when it comes to industrial and environmental safety.
At its core, aluminum sulfate is produced by reacting two main ingredients:
These ingredients are chosen for their availability and ability to yield high-purity aluminum sulfate. The quality of the starting materials directly impacts the final product’s effectiveness—especially in sensitive applications like drinking water purification or paper manufacturing [EPA].
Sounds complex? The chemistry is surprisingly straightforward. When aluminum hydroxide reacts with sulfuric acid, aluminum sulfate and water are formed. Here’s the core equation:
2Al(OH)3 + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 6H2O
Sometimes, the process starts with bauxite instead of pure aluminum hydroxide, especially when cost or resource availability dictates. In either case, the reaction is carried out in a controlled reactor, with careful attention to temperature and mixing to ensure complete conversion and high purity [NZIC].
Let’s walk through the typical aluminum sulfate production process:
Not all aluminum sulfate is created equal. The purity of raw materials and the precision of the production process determine which grade is suitable for specific industries. For example:
| Grade | Typical Use | Purity Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Drinking Water Grade | Municipal water treatment | Low heavy metals, high solubility, NSF/ANSI certification |
| Papermaking Grade | Pulp and paper mills | Low iron and silica for paper brightness and strength |
| Industrial Grade | Textiles, construction, agriculture | May tolerate higher levels of some impurities |
For high-stakes uses—like purifying drinking water or manufacturing premium paper—even trace contaminants can cause major issues. That’s why producers invest in rigorous quality control and source the purest possible raw materials.
Imagine you’re designing materials for rail transit or high-tech construction. Just as aluminum sulfate quality depends on its raw materials and process, so does the performance of aluminum profiles in engineering applications. Leading manufacturers like Shengxin Aluminum exemplify the importance of advanced production lines, strict quality control, and investment in technology. Their approach mirrors the best practices in chemical manufacturing, where every step—from sourcing to final inspection—ensures the end product meets demanding industry standards.
Understanding how aluminum sulfate is made—and why purity matters—sets the stage for exploring its diverse uses. Up next, we’ll look at the many ways this compound supports industries and homes around the world.
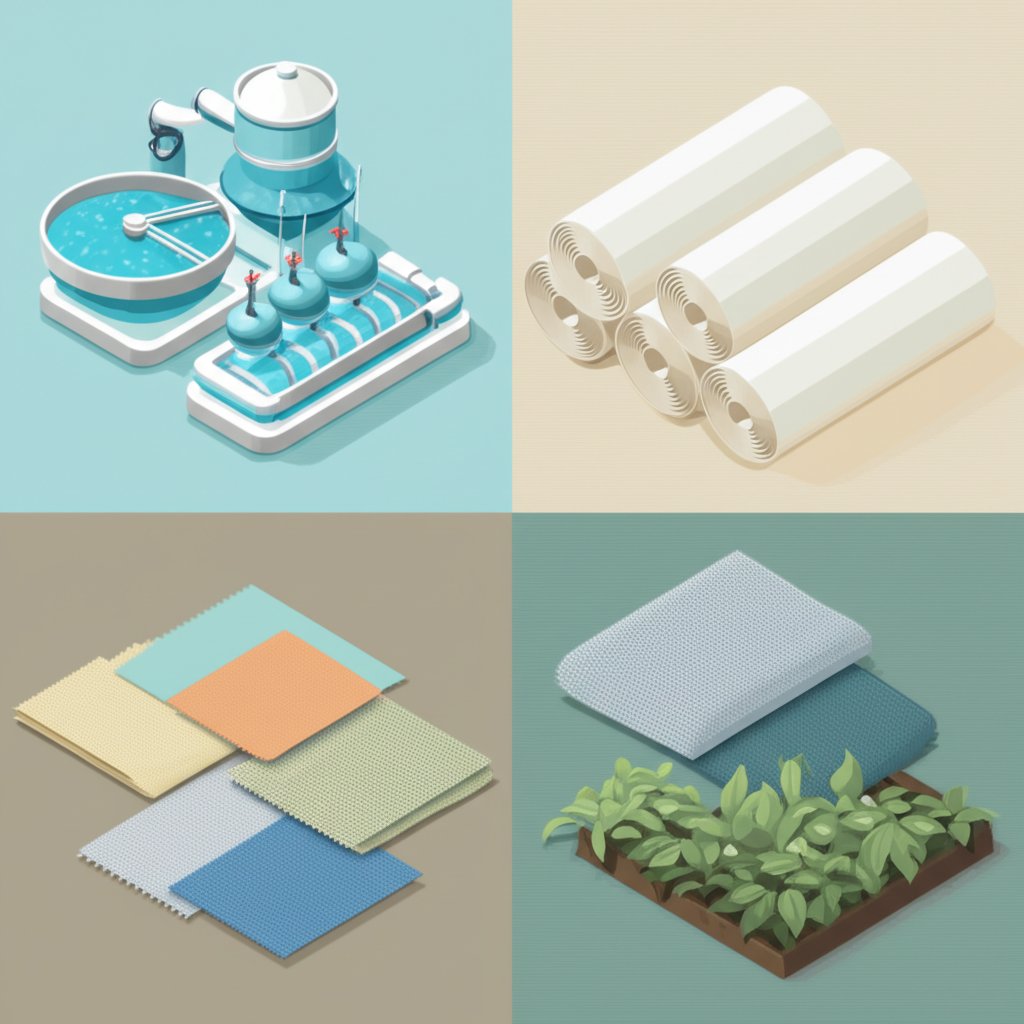

When you open your tap for a glass of clear water or notice your garden’s hydrangeas blooming in vibrant blue, you’re seeing the subtle influence of aluminum sulfate at work. But what is aluminum sulfate used for beyond these familiar scenes? Let’s explore its wide-ranging applications, from the heart of industry to the comfort of your home.
Aluminum sulfate is a true workhorse in many sectors, thanks to its ability to purify, bind, and react in ways that support essential processes. Here’s a breakdown of where you’ll find it most:
It’s not just factories and treatment plants that benefit. You’ll also find aluminum sulfate in:
| Sector | Primary Functions | Typical Products/Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Water Treatment | Flocculant, impurity removal | Drinking water, wastewater, pools |
| Pulp & Paper | Sizing agent, improves print quality | Books, packaging, specialty papers |
| Textiles | Mordant for dye fixation | Colored fabrics, printed cloth |
| Construction | Additive for strength, fire resistance | Concrete, fire-retardant foams |
| Pharmaceuticals | Astringent, protein precipitant | Antiperspirants, styptic pencils, some medications |
| Household/Gardening | Soil pH adjustment, personal care | Garden soil, deodorants, baking powder |
Imagine the impact if low-quality aluminum sulfate were used in water treatment—impurities could slip through, or paper might not hold ink well. This is why industries demand high-grade, precisely manufactured chemicals. The same attention to quality and specialized production is critical in the aluminum industry. For a deeper dive into these connections, check out this insightful blog from Shengxin Aluminum: Essential Insights on Aluminum Sulfate: Key Uses.
Companies like Shengxin Aluminum exemplify how advanced technology and strict quality control can elevate not just aluminum profiles for construction and transportation, but also the reliability of essential chemicals like aluminum sulfate across industries. This commitment to excellence ensures that the materials and products you rely on—whether it’s safe water, sturdy buildings, or vibrant textiles—meet the highest standards.
Curious about more specialized uses, like how aluminum sulfate helps maintain sparkling pools or supports healthy gardens? Let’s dig into these practical benefits in the next section.
Ever stared at a murky pool or struggled to grow acid-loving plants in stubborn soil? If so, aluminum sulfate might be your secret weapon. Let’s break down what is aluminum sulfate for pools and what is aluminum sulfate used for in gardening—with clear, actionable steps and tips for success.
Imagine opening your pool after winter, only to find the water cloudy or green. That’s where aluminum sulfate steps in as a powerful flocculant. But how does it work?
Step-by-Step: Using Aluminum Sulfate in Pools
Precautions & Tips:
Ever wonder why your hydrangeas aren’t blue, or your azaleas look unhappy? The answer could be your soil’s pH. Many prized plants—like blueberries, rhododendrons, and azaleas—need acidic soil (pH 5.5 or lower). Here’s where aluminum sulfate shines:
Guidelines for Use:
Warnings & Tips:
Whether you’re tackling a murky pool or coaxing blue blooms from your hydrangeas, aluminum sulfate offers a targeted, effective solution. Up next, discover how related compounds—like sodium and potassium aluminum sulfate—expand the possibilities even further.
When you hear the word “alum,” you might picture a white powder in your kitchen, a crystal deodorant rock, or even a laboratory jar. But did you know there are several types of alum, each with its own formula and specialty uses? Two of the most common are sodium aluminum sulfate and potassium aluminum sulfate. Let’s break down what is sodium aluminum sulfate and what is potassium aluminum sulfate, how they differ from classic aluminum sulfate, and where you’ll find each in everyday life.
Sodium aluminum sulfate—often called soda alum—is an inorganic compound with the formula NaAl(SO4)2·12H2O. It appears as a white crystalline powder and is highly soluble in water. One of its best-known roles is in the food industry, where it’s used as a component of some baking powders and as a food additive (E number E521) to regulate acidity. In addition, it serves as a mordant in textile dyeing and as a flocculant in industrial water treatment, though its more caustic nature makes it less common for municipal water purification [reference].
Potassium aluminum sulfate—better known as potash alum—has the formula KAl(SO4)2·12H2O. This is the classic “alum” found in grocery store spice aisles and pickling recipes. Potash alum is prized for its ability to help dyes adhere to fabrics, purify water, and act as an astringent in aftershaves and deodorants. You’ll also find it in fireproofing textiles, and as a pickling agent to keep vegetables crisp [reference].
While all three compounds contain aluminum and sulfate ions, the presence of sodium or potassium changes their properties and applications. Aluminum sulfate itself (Al2(SO4)3) is not technically an alum, but it’s closely related and widely used in water treatment, paper manufacturing, and soil amendment.
| Compound | Chemical Formula | Main Cation | Key Uses | Typical Sectors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Sulfate | Al2(SO4)3 (often hydrated) | Aluminum (Al3+) | Water purification, papermaking, soil pH adjustment | Municipal, industrial, agriculture |
| Sodium Aluminum Sulfate (Soda Alum) | NaAl(SO4)2·12H2O | Sodium (Na+) | Baking powder, acidity regulator, textile mordant | Food, textiles, industry |
| Potassium Aluminum Sulfate (Potash Alum) | KAl(SO4)2·12H2O | Potassium (K+) | Water purification, dye mordant, pickling, astringent | Food, water, cosmetics, textiles |
In summary, if you’re baking with double-acting powder, dyeing fabrics, or purifying water, you’re likely benefiting from one of these specialized aluminum sulfate relatives. Their subtle differences in composition unlock a world of unique uses, from your kitchen to your laundry room—and beyond. Next, let’s explore even more specialized aluminum sulfate-related compounds and how they expand this family’s reach in science and industry.
Ever come across a chemical name that sounds even more complex than aluminum sulfate? You’re not alone! The world of aluminum sulfate-related compounds is surprisingly diverse, with each variation offering unique properties and uses. Let’s dive into two notable members of this family: amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate and aluminum hydrogen sulfate.
Imagine a material designed specifically for high-tech medical applications—this is where amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate (often abbreviated as AAHS) steps in. Unlike classic aluminum sulfate, AAHS is a specially engineered, non-crystalline (amorphous) compound that contains aluminum, phosphate, hydroxide, and sulfate ions. Its structure can be represented as a mix of aluminum hydroxyphosphate with sulfate groups incorporated, giving it a unique balance of properties.
Why use AAHS instead of other aluminum salts? Its amorphous nature and fine particle size enhance its ability to adsorb vaccine components, making it a flexible and reliable platform for modern immunizations.
Now, let’s tackle another specialized compound: aluminum hydrogen sulfate. The name might sound intimidating, but its structure is straightforward—it’s essentially aluminum sulfate where hydrogen ions are associated with the sulfate groups, giving it the formula AlH3O12S3 [PubChem].
The aluminum sulfate family doesn’t stop at just one formula. From amorphous forms used in life-saving vaccines to hydrogen sulfate salts with niche industrial roles, these compounds demonstrate how small changes in composition can unlock new possibilities. Whether you’re researching what is amorphous aluminum hydroxyphosphate sulfate for pharmaceutical development, or encountering aluminum hydrogen sulfate in a chemistry lab, it’s clear that this group of chemicals plays a vital, adaptable role in science and industry.
Next, we’ll wrap up by summarizing the importance and broad applications of aluminum sulfate and its relatives—highlighting how quality and innovation continue to shape their impact in our daily lives.
Have you ever stopped to consider how a single compound can quietly shape so many aspects of modern life? From the water you drink to the paper you write on, aluminum sulfate is a behind-the-scenes powerhouse. Let’s recap why this compound deserves our attention—and how its story connects science, industry, and innovation.
Why is aluminum sulfate importance so widely recognized across industries? It’s about more than just chemistry—it’s about the pursuit of quality and the drive for innovation. Industries rely on high-purity, precisely manufactured aluminum sulfate to meet demanding standards, protect public health, and enable new technologies [Affinity Chemical]. The continued evolution of its production and use—such as eco-friendly manufacturing or advanced applications in textiles and pharmaceuticals—shows how even familiar materials can be reimagined for a better future [Aseda Chemicals].
Leading companies like Shengxin Aluminum exemplify the value of investing in advanced production lines, strict quality control, and research partnerships. Just as precision matters for aluminum profiles in construction and transportation, it’s equally vital for the chemicals that underpin our infrastructure, environment, and health.
Next time you turn on the tap, walk through a city, or see vibrant colors in textiles and gardens, imagine the invisible science at work. Aluminum sulfate’s story is a reminder to value the research, technology, and quality standards that make modern life possible. As industries continue to innovate, the humble compounds behind the scenes—like aluminum sulfate—will keep playing a key role in shaping a safer, cleaner, and more sustainable world.
Aluminum sulfate is generally considered non-toxic under normal handling. However, it can cause irritation or burns if it comes into contact with skin, eyes, or is inhaled as dust. Prolonged exposure may lead to respiratory discomfort. While not classified as a carcinogen, always use protective equipment and follow safety guidelines when handling it.
Aluminum sulfate is approved as a food additive in some regions, where it serves as a firming agent (E520). The FDA recognizes it as generally safe for use in food processing at regulated levels. However, its use is limited and monitored to ensure consumer safety.
In water treatment, aluminum sulfate acts as a flocculant, helping to bind and remove impurities from drinking water and wastewater. It causes suspended particles to clump together, making it easier for filtration systems to remove contaminants, resulting in clearer and safer water.
Aluminum sulfate lowers soil pH, making it more acidic. This is especially helpful for acid-loving plants like hydrangeas and azaleas, promoting better growth and more vibrant blooms. Overuse should be avoided, as excessive acidity can harm some plants; always test soil before application.
Aluminum sulfate (Al₂(SO₄)₃) is primarily used for water purification, paper manufacturing, and soil amendment. Potash alum, or potassium aluminum sulfate (KAl(SO₄)₂·12H₂O), is commonly found in food, cosmetics, and textile dyeing. The key difference lies in the presence of potassium in potash alum, which changes its properties and typical uses.
 Інтернет-сервіс
Інтернет-сервіс 0086 136 3563 2360
0086 136 3563 2360 sales@sxalu.com
sales@sxalu.com +86 136 3563 2360
+86 136 3563 2360